What is the CPI and How is it Calculated?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI), also known as Índice de Precios al Consumidor (IPC) in Spanish, is a crucial economic indicator in the United States. It measures the monthly variation in prices paid by consumers and is used to calculate inflation in the economy. Here’s how it is calculated:
-
Basket of Goods and Services:
- The CPI is based on a basket of goods and services representative of urban household consumption.
- This basket includes products such as food, housing, transportation, healthcare, education, and more.
-
Data Collection:
- Price data is collected from thousands of establishments across the country.
- Prices are updated regularly to reflect market trends.
-
Weight Allocation:
- Each item in the basket is assigned a weight according to its importance in total consumer spending.
- For example, rent may have a greater weight than the cost of a coffee.
-
Calculation Formula:
-
The CPI is calculated using a specific mathematical formula:
CPI = Base Cost of the Basket / Current Cost of the Basket × 100
- The current cost of the basket is the total price of the goods and services in the current period.
- The base cost of the basket is the total price in a previous reference period (usually taken as 1982-1984).
-
The CPI is calculated using a specific mathematical formula:
-
Monthly and Annual Variation:
- The CPI is published monthly and shows the price variation from the previous month.
- The annual variation rate compares the current CPI with the same month of the previous year.
-
Interpretation:
- If the CPI rises, it indicates inflation; if it falls, deflation.
- The Federal Reserve of the United States aims to keep inflation around 2% annually.
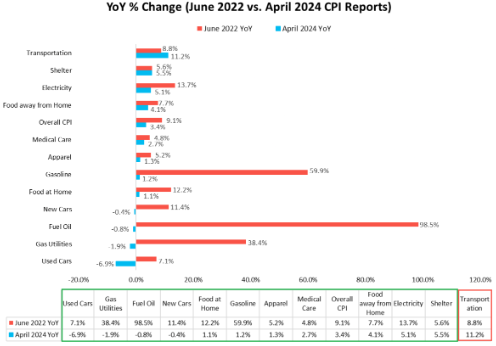
Price evolution compared to last year (April CPI report)
- Transportation: +11.2%
- Shelter: +5.5%
- Electricity: +5.1%
- Food away from home: +4.1%
- Overall CPI: +3.4%
- Healthcare: +2.7%
- Gasoline: +1.2%
- Food at home: +1.1%
- New cars: -0.4%
- Fuel oil: -0.8%
- Utility gas services: -1.9%
- Used cars: -6.9%
Increases in the last 4 years
- CPI Healthcare: +9.1%
- CPI Apparel: +13.0%
- Wages in the U.S.: +16.1%
- CPI New Automobiles: +21.3%
- CPI Food at Home: +21.5%
- CPI Housing: +22.4%
- CPI Food Away from Home: +25.9%
- CPI Used Vehicles: +30.9%
- CPI Electricity: +31.2%
- CPI Utility Gas Services: +33.7%
- CPI Transportation: +41.5%
- Real Estate Prices: +46.4%
- CPI Fuel Oil: +72.7%
- CPI Gasoline: +91.2%
The U.S. inflation rate (CPI) has dropped from a peak of 9.1% in June 2022 to the current 3.4%.
What is Driving this Decline?
Lower inflation rates in used cars, utility gas services, fuel oil, new cars, food at home, gasoline, clothing, healthcare, food away from home, electricity, and shelter.
Transportation is the only major component that has a higher inflation rate today than in June 2022.
How Does the CPI Affect Consumers?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) has a significant impact on consumers' lives. Let me explain how it affects them:
-
Purchasing Power:
- Inflation, measured by the CPI, directly affects consumers' purchasing power.
- When prices rise, money doesn't go as far since we have to pay more for the same goods and services.
-
Cost of Living:
- The CPI reflects changes in the cost of living.
- If inflation increases, consumers face higher costs to maintain their usual standard of living.
-
Specific Expenses:
-
Some categories of expenses are more affected than others:
Energy: Gasoline prices can vary significantly. Although they have risen recently, they may stabilize as fuel production increases.
Food: Food prices also fluctuate. Shortages and production issues can influence their cost.
Other Goods and Services: The CPI affects the price of appliances, clothing, healthcare, and more.
-
Some categories of expenses are more affected than others:
-
Investments:
- Investors must consider inflation when making financial decisions.
- Understanding the effect of the CPI on investments can help generate better outcomes.
-
Financial Planning:
- Consumers must adjust their budgets according to inflationary trends.
- Staying informed about changes in the CPI is essential for good financial planning.
